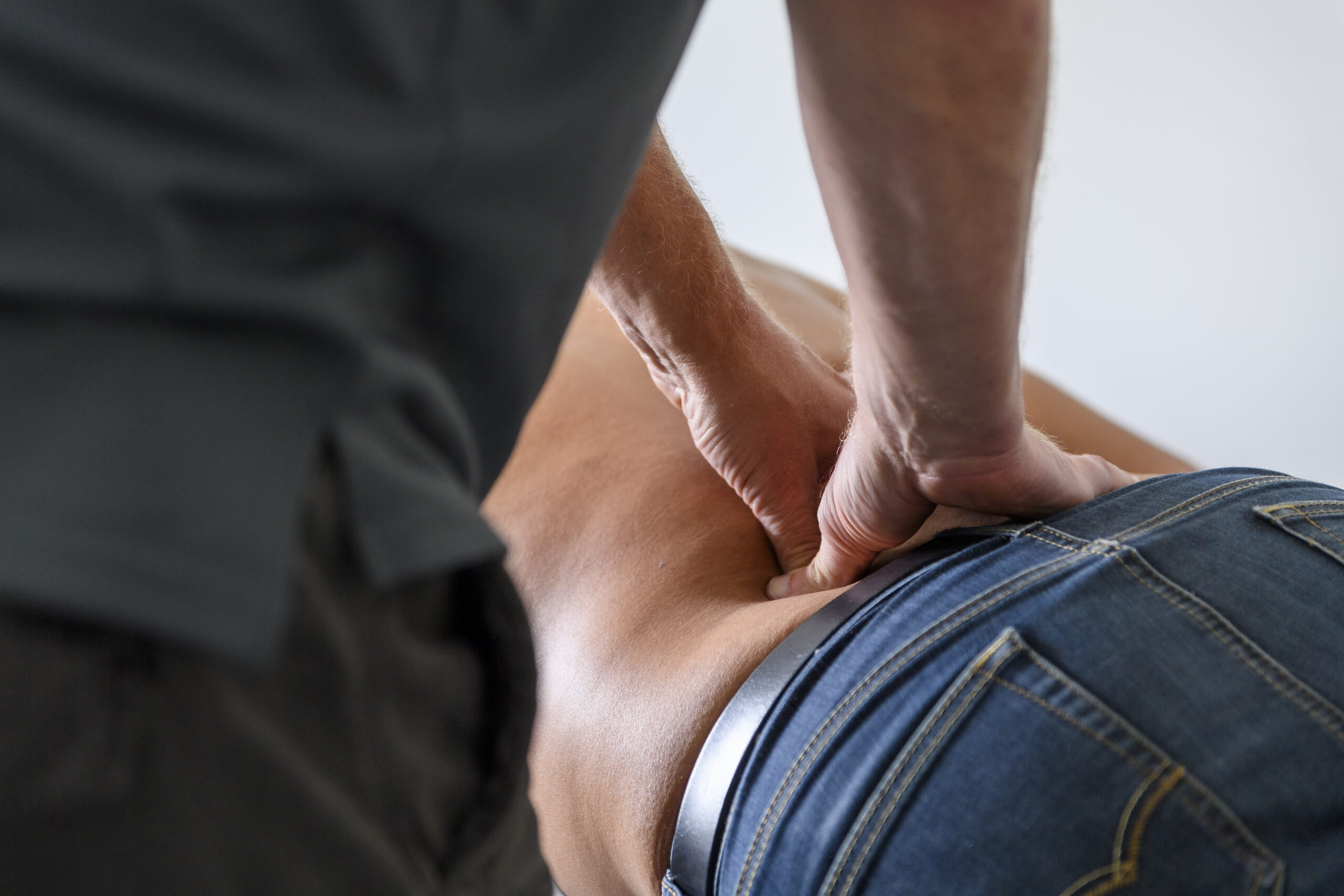
What does
Hands-on mean?
Years of experience shows us the benefits when used alongside good management advice and tailored exercise.
Hands-on Physiotherapy or manual therapy techniques can involve a number of different techniques, used independently or blended together to give comfortable effective treatment.
Manual therapy has a long history within the profession of Physiotherapy, and Physiotherapists have continued to develop manual therapy approaches and techniques leading to an expanse of available skills.
Historically, the benefits of providing hands-on examination and intervention were explained as purely mechanical, but contemporary research reveals additional neurophysiological and psychological mechanisms are also involved.
We recognise that Physiotherapists are best placed to achieve all of these benefits. A skilled and experienced hands-on approach and knowledge of anatomy and physiology allows targeted assessment and treatment, impacting you and your body’s muscles, bones, joints, fascia, and nerves.
Some examples of manual therapy techniques we might use:
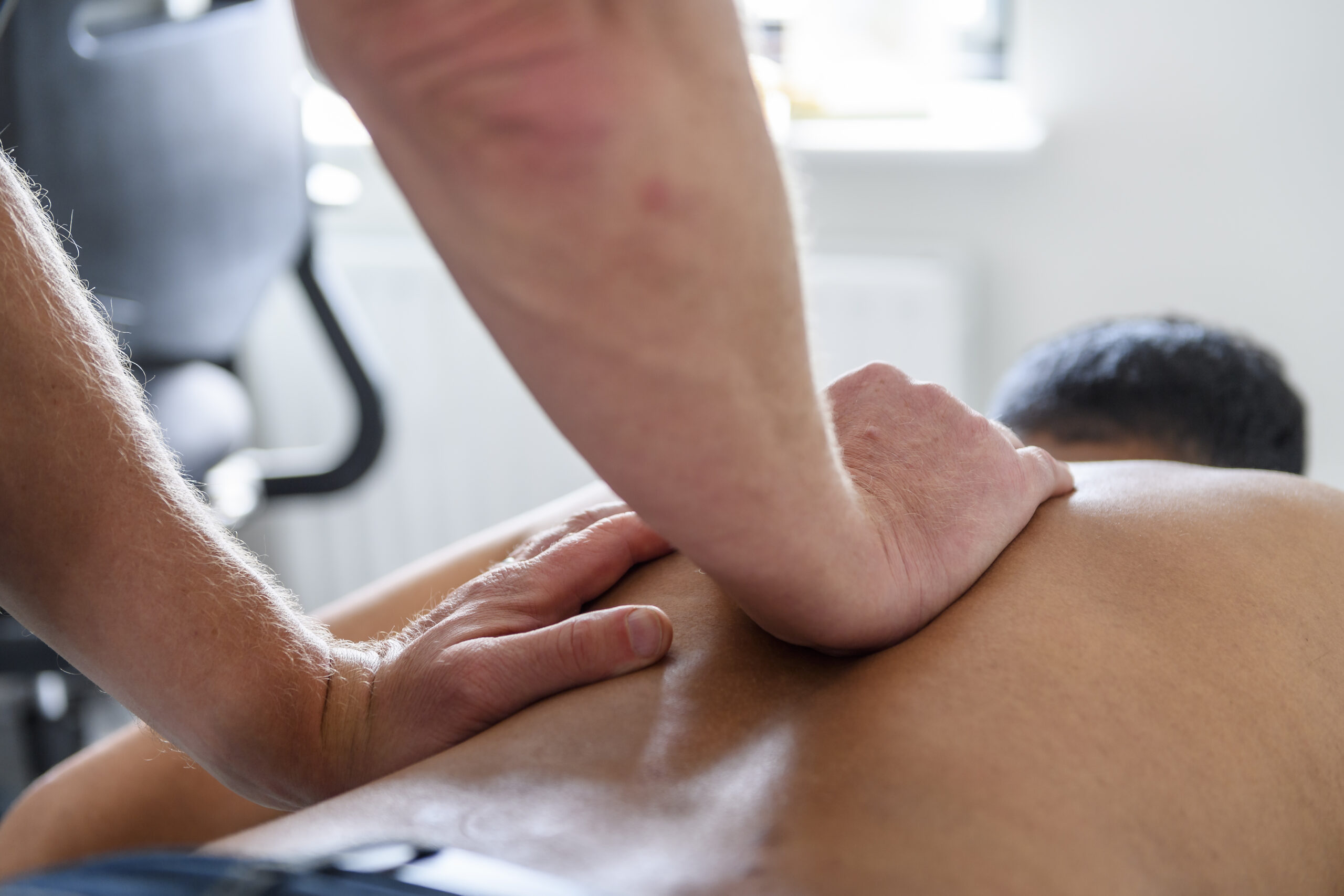
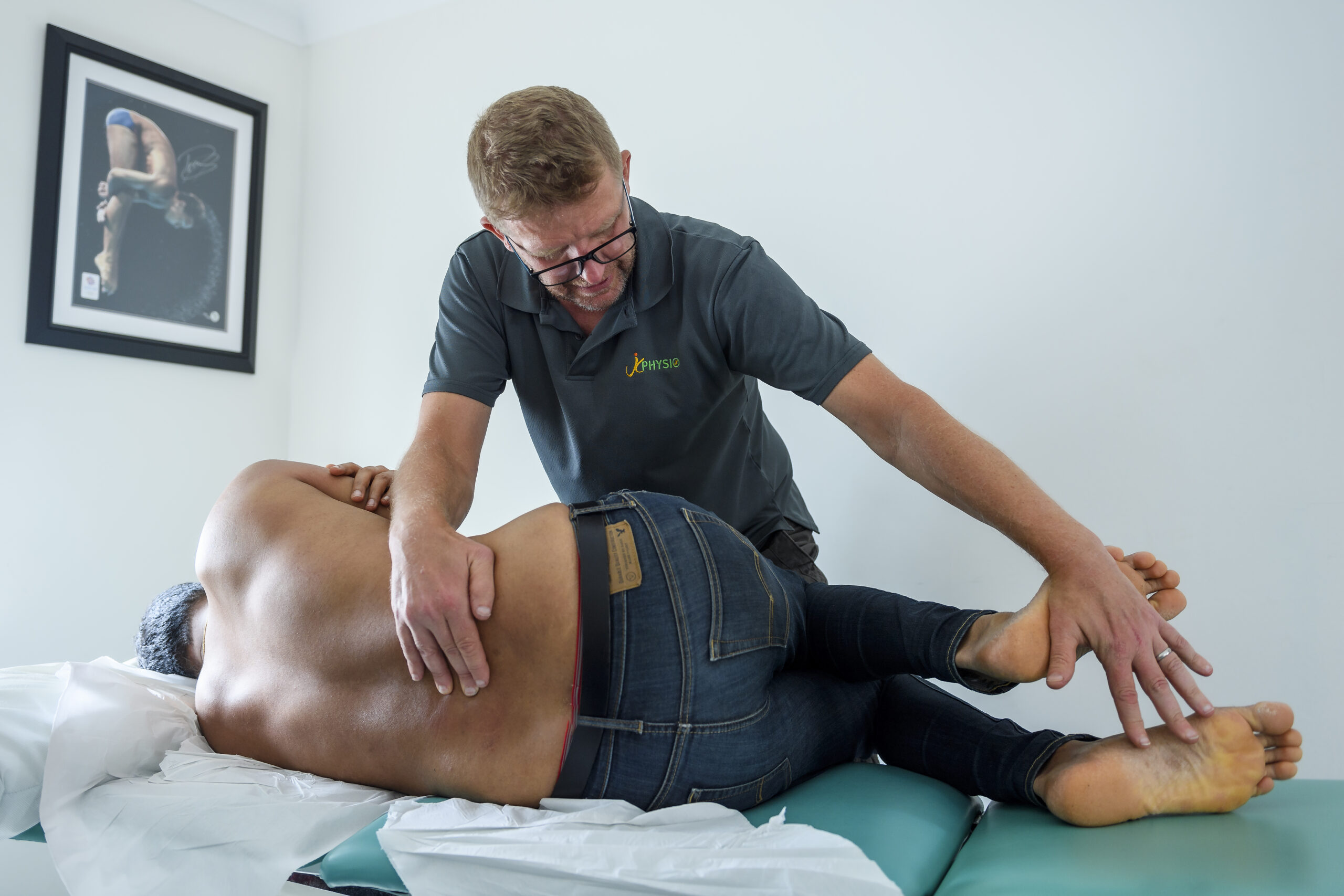
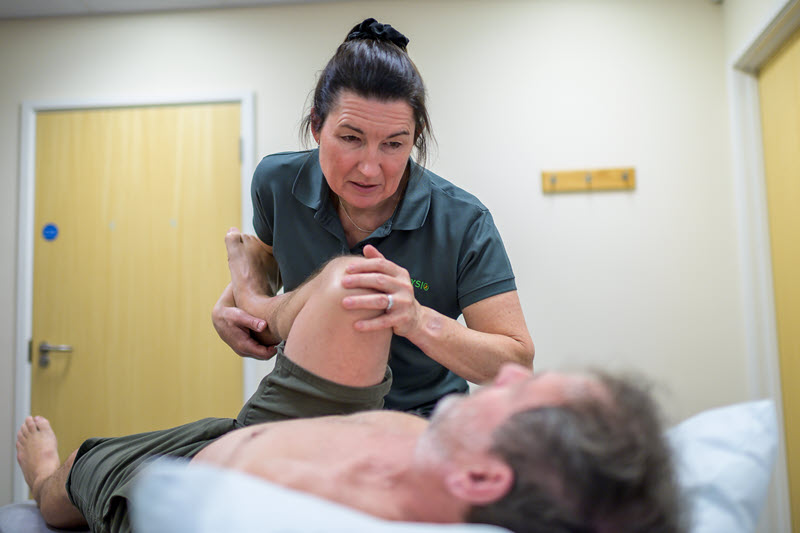
Some examples of manual therapy frameworks we draw from within our treatments:
Hands-on Physiotherapy or manual therapy techniques can involve a number of different techniques used either independently or blended together to give comfortable effective treatment.
Assessment and treatment might include techniques such as:
Cyriax:
A system of examination and intervention that aims to address nonsurgical, soft tissue lesions through the concept of Selective Tissue Tension (STT) testing and differential diagnosis.
Treatment methods include manipulation, traction and friction techniques.
Maitland Manual Therapy:
Prioritises ‘clinical evidence rather than a given diagnosis’. High level of problem solving and clinical reasoning to constantly develop a clinical hypothesis throughout examination and re-examination. Techniques are non-prescriptive and can be modified, reversed and enhanced. Passive mobilisations use oscillatory movement and emphasis movement perception.
Treatment methods include rhythmic, passive, painless movements (mobilisations) and rapid movements (manipulations).
Mulligan Manual Therapy:
Based on active patient movements combined with passive correction of the joint position held by a Physiotherapist.
Treatment methods include active combined with passive correction of the joint position held by a Physiotherapist.
Kaltenborn-Evjenth Manual Therapy:
Uses translatory joint movements in association with the treatment plane in both assessment and diagnosis. Translatory traction, compression and gliding joint play movements are applied based on convex- concave theory to assess joint function, translatory gliding and traction mobilisations are used to restore joint play to its usual state.
Treatment methods include transverse massage, functional massage, post-isometric relaxation, joint mobilisation and neural mobilisation.
Mechanical Diagnosis and Therapy (McKenzie Method):
Uses repeated or sustained movements to decrease and abolish symptoms and return to function.
Treatment methods involve directed specific movements guided by classification of painful movement patterns found.
Lewit Manual Therapy:
Dysfunctions are viewed as part of a chain of interrelated pathologies.
Treatment methods include mobilising, manipulating and active exercise.
JK Physio has been exceptional – with caring and efficient staff. They are very polite and over the years I have been coming the physiotherapy has helped me so much to keep me active.